元组是python内置数据结构之一,是一个不可变序列。
元组的特点:有序,可多种不同数据类型的元素混合存储,允许有重复数据,是不可变序列(所以没有元组生成式)。
创建元组的四种方式
1)使用(),元素用英文版的逗号隔开
语法格式:tuple_name = (element, element, ……, element)
元素之间使用英文版的逗号隔开。()可以省略。
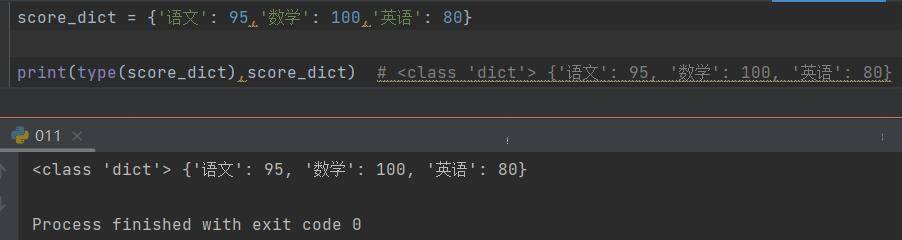
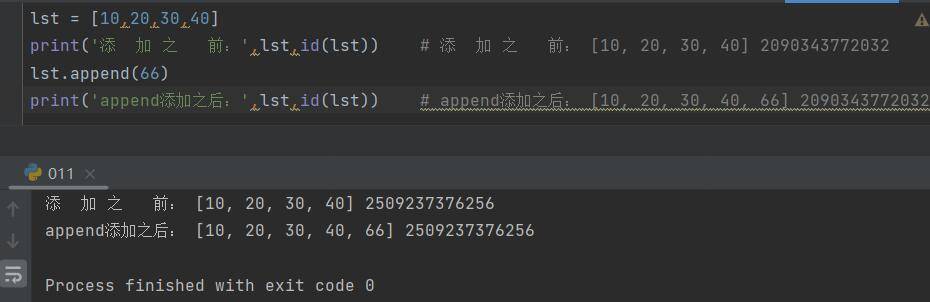
t1 = ('hello','python',80,'world')
print(t1,type(t1)) # ('hello', 'python', 80, 'world') <class 'tuple'>
# 多个元素,()可以省略
t2 = 'hello','python',80,'world'
print(t2,type(t2)) # ('hello', 'python', 80, 'world') <class 'tuple'>![图片[1]-Python 元组的创建和查询操作详解-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/ca05e446b7160159.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
2)使用内置函数 tuple()
语法格式:tuple_name = tuple(iterable)
参数说明:
iterable:要转换成元素的可迭代序列。
返回值:返回一个元组。
将某个可迭代序列转换成元组。
t1 = tuple(('hello','python',80,'world'))
print(t1,type(t1))
# tuple()将其他数据类型转换成了元组类型
t2 = tuple([10,20,'aba','hello',99])
print(t2,type(t2))
t3 = tuple({'world','name',100,222})
print(t3,type(t3))
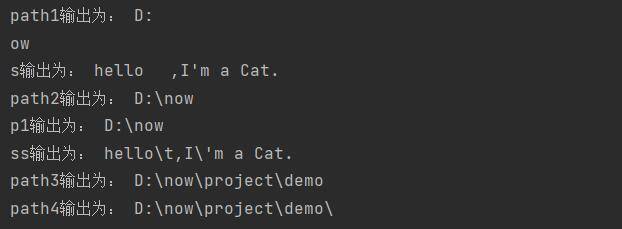
t4 = tuple('hello')
print(t4,type(t4))![图片[2]-Python 元组的创建和查询操作详解-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/99a693276f160907.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
3)创建只包含一个元素的元组
语法格式:tuple_name = (element,)
元素后面逗号不能省略!!!
注意:
t2 = ('python')
print(type(t2),t2) # <class 'str'> python
# ,不能省略,否则就会被认为是它(那个元素)本身的数据类型
t3 = ('python',)
print(type(t3),t3) # <class 'tuple'> ('python',)
# ()可以省略,但,不能省
t4 = 'python',
print(type(t4),t4) # <class 'tuple'> ('python',)![图片[3]-Python 元组的创建和查询操作详解-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/e23c46d072162213.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
观察代码输出结果可以看出:省略了逗号的,输出的是 str 类型。而添加了逗号的,输出的是 tuple 类型。
4)创建空元组
创建空元组有两种方式,一种是(),一种是使用内置函数tuple()。
代码演示:
t1 = ()
print(type(t1),t1) # <class 'tuple'> ()
t2 = tuple()
print(type(t2),t2) # <class 'tuple'> ()![图片[4]-Python 元组的创建和查询操作详解-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/9bec9cf84f162536.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
元组的查询操作
1)[] —-> 查询单个元素, 适合知道元素个数,否则越界会抛出异常
语法格式:tuple_name[index]
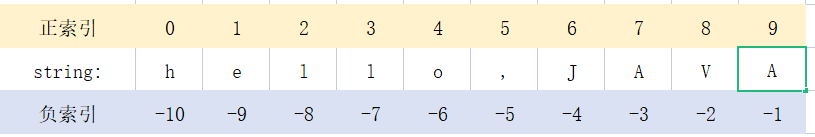
元组是有序的,所以可以通过索引号来访问元组中的元素。而索引又分为正向索引(index>=0)和逆向索引(index<0)。
t = ('hello','python',80,'world')
print(t[1]) # python
print(t[-2]) # 80![图片[5]-Python 元组的创建和查询操作详解-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/c09a2cb477172418.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
如果索引越界(index > len(tuple_name)),会抛出异常 IndexError。
t = ('hello','python',80,'world')
print(t[6]) # IndexError: tuple index out of range![图片[6]-Python 元组的创建和查询操作详解-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/87b26dd9ad172512.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
2)for循环遍历元组 不知道元素个数
t = ('hello','python',80,'world')
for i in t:
print(i)![图片[7]-Python 元组的创建和查询操作详解-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/59252149ad172740.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
3)使用in/not in判断指定元素是否存在
t = ('hello','python',80,'world')
print(80 in t) # True
print('hello' in t) # True
print(999 in t) # False![图片[8]-Python 元组的创建和查询操作详解-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/f09fe6e45e172957.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
4)切片操作 —–> 查询某个片段的元素
语法格式:new_tuple = tuple_name[start:stop:step]
得到左闭右开区间 [start, stop) 之间的元素组成的新元组。
t = ('hello','python',80,'world','hello')
# [0,3)之间的元素,返回一个新的元组
c = t[:3]
print(c)
# 负索引
print(t[-4:-2])![图片[9]-Python 元组的创建和查询操作详解-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/c65bea8196195720.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
为什么把元组设为不可变序列?
因为一旦创建了不可变对象,对象内部的所有数据就都不能被修改,这样可以避免由于修改数据而导致的错误。并且,对于不可变对象,在多任务环境下,同时操作对象的时候就不需要加锁。
需要注意的是,在元组中存储的是对象的引用,如果元组中的对象本身是不可变对象,那么元组中的元素不可以更改;如果元组中的对象本身是可变对象,那么这个可变对象的引用可以不允许改变,其中的数据可以改变。
在程序中要尽量使用不可变序列。
1 本站一切资源不代表本站立场,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责。
2 本站一律禁止以任何方式发布或转载任何违法的相关信息,访客发现请向站长举报。
3 本站资源大多存储在云盘,如发现链接失效,请联系我们我们会第一时间更新。





暂无评论内容