1、获取指定元素的索引 —> index()
语法结构:
lst_name.index(element[,start,stop])
参数说明:
element:要查询的元素。
start :查询的起始位置。
stop:查找的结束位置,不包含stop。
start和stop都可省略,省略后默认查找整个列表。
若所查询的列表中有N个相同的元素,只返回相同元素的第一个元素的索引。如果查询的元素在列表中不存在,则抛出异常ValueError。
lst = ['hello','python',10,'hello',22]
# 若所查询的列表中有N个相同的元素,只返回相同元素的第一个元素的索引
print(lst.index('hello')) # 0
# 在指定的start和stop之间进行查找:这个查找范围不包含stop
# 在索引[1,4)之间查找'hello'
print(lst.index('hello',1,4)) # 3如果查询的元素在列表中不存在,则抛出异常ValueError:
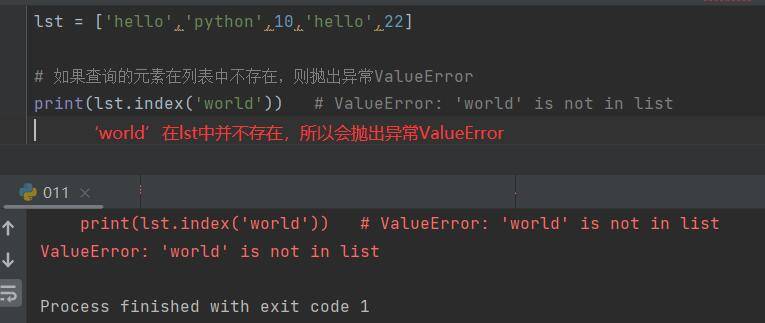
lst = ['hello','python',10,'hello',22]
# 如果查询的元素在列表中不存在,则抛出异常ValueError
print(lst.index('world')) # ValueError: 'world' is not in list![图片[1]-Python列表的五种常用的查询方式(获取元素)-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/aeb4bf9cf5165122.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
2、获取单个元素 —> [索引号]
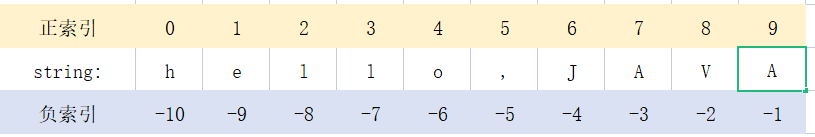
列表是有序的,所以可以根据索引号获取单个元素。索引又分为正向索引(0~N-1)和逆向索引(-N~-1),如果指定的索引不存在,则抛出IndexError。
lst = ['hello','world',90,'hello','python',10]
# 正向索引0~N-1
print(lst[2]) # 90
# 逆向索引-N~-1
print(lst[-3]) # hello
# 如果指定的索引不存在,则抛出IndexError。
print(lst[8]) # IndexError: list index out of range如果指定的索引不存在,则抛出IndexError。
lst = ['hello','world',90,'hello','python',10]
# 如果指定的索引不存在,则抛出IndexError。
print(lst[8]) # IndexError: list index out of range![图片[2]-Python列表的五种常用的查询方式(获取元素)-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/750c85c630171155.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
3、获取多个元素 —> 切片操作
通过切片操作可以得到原列表片段的拷贝,这是一个新的列表对象。它的范围是一个左闭右开的区间[start,stop)。
语法规则:list_name[start:stop:step]
![图片[3]-Python列表的五种常用的查询方式(获取元素)-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/10/d1d3648731182949.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
代码演示
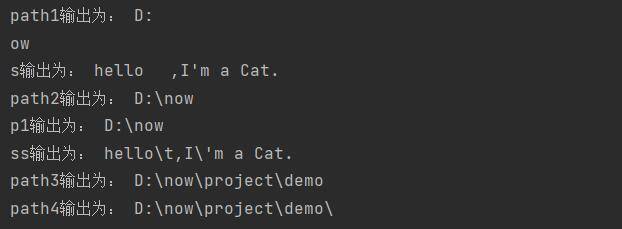
lst = [0,10,20,30,40,50,60,70,80,90]
# step为默认值1
print(lst[2:6]) # [20, 30, 40, 50]
# step为正数,从start开始往后计算
print(lst[2:8:2]) # [20, 40, 60]
# stop默认是列表的最后一个元素
print(lst[2::2]) # [20, 40, 60, 80]
# start默认是列表的第一个元素
print(lst[:8:2]) # [0, 20, 40, 60]
# 顺序截取列表全部元素
print(lst[::]) # [0, 10, 20, 30, 40, 50, 60, 70, 80, 90]
# step为负数,从start开始往前计算
print(lst[5:9:-1]) # [] 从右往左切片,start要大于stop,否则切不出数据
print(lst[5:2:-1]) # [50, 40, 30]
# stop默认是列表的第一个元素
print(lst[6::-1]) # [60, 50, 40, 30, 20, 10, 0]
# start默认是列表的最后一个元素。
print(lst[:2:-2]) # [90, 70, 50, 30]
# 逆向索引
print(lst[-2:-6:-1]) # [80, 70, 60, 50]
# 逆序截取列表全部元素
print(lst[::-1]) # [90, 80, 70, 60, 50, 40, 30, 20, 10, 0]运行结果:
![图片[4]-Python列表的五种常用的查询方式(获取元素)-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/1e9360a5ba005620.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
![图片[5]-Python列表的五种常用的查询方式(获取元素)-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/6d24b9d826005639.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
4、in/not in 判断指定元素在列表中是否存在
1) in
语法格式:元素 in 列表名
元素在列表中则返回True,否则返回False。
lst = ['hello','python',10,'hello',22]
# 10在lst列表中,所以为真True
print(10 in lst) # True
# 'world'不在lst列表中,所以为假False
print('world' in lst) # False2)not in
语法格式:元素 not in 列表名
元素不在列表中返回True,否则返回False。
lst = ['hello','python',10,'hello',22]
# 'python'在lst列表中,所以为假False
print('python' not in lst) # False
# # 99不在lst列表中,所以为真True
print(99 not in lst) # True5、count()
语法格式:list_name.count(element)
参数说明:element 表示要查找的元素。
方法说明:用于统计某个元素在列表中出现的次数,如果查找的元素不存在,则返回0。
返回值:返回某个元素在列表中出现的次数。
代码演示:
lst = ['hello','python',10,'hello',22,'java',10,10]
result = lst.count('hello')
print('元素hello出现的次数:',result)
result1 = lst.count(10)
print('元素10出现的次数:',result1)
result2 = lst.count(999)
print(result2)![图片[6]-Python列表的五种常用的查询方式(获取元素)-尤尤'blog](https://pic.yxfseo.cn/wp-content/uploads/2022/11/ca5894b1ac011737.jpg?imageView2/0/interlace/1/q/75|imageslim)
© 版权声明
本站网络名称:
尤尤博客
本站永久网址:
https://www.yxfseo.cn
网站侵权说明:
本网站的文章部分内容可能来源于网络,仅供大家学习与参考,请在24H内删除。
1 本站一切资源不代表本站立场,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责。
2 本站一律禁止以任何方式发布或转载任何违法的相关信息,访客发现请向站长举报。
3 本站资源大多存储在云盘,如发现链接失效,请联系我们我们会第一时间更新。
1 本站一切资源不代表本站立场,并不代表本站赞同其观点和对其真实性负责。
2 本站一律禁止以任何方式发布或转载任何违法的相关信息,访客发现请向站长举报。
3 本站资源大多存储在云盘,如发现链接失效,请联系我们我们会第一时间更新。
THE END




暂无评论内容